Theme: Exploring Current Research Innovations and Interactive discussion on Radiology and Oncology Research
Radiology and Oncology 2018
- About Radiology and Oncology 2018 Conference
- Sessions/Tracks
- Market Analysis Report
- New Updates: Radiology and Oncology 2018
- Radiology Diagnose for diseases
- Past Conference Report
Radiology and Oncology 2018 Congress
On behalf of the Scientific Committee, we are honored to invite you to 2nd World Congress on Radiology and Oncology to be held in the Dubai, UAE during July 16-17, 2018.
The Theme of the Radiology and Oncology -2018 is “Innovations and future directions in Radiology and Oncology" which covers the wide range of critically important sessions in the field of Radiology, Oncology, Cancer, and Imaging. The objective of this meeting is to share the foremost updated knowledge on the radiology and the novel therapeutic options in Cancer treatment. We will gather academicians and young inspired scientists from all around the world involved in researchers at the cutting edge in the study of the radiology and oncology.
The conference proceedings will include seminars, symposiums, Oral Presentations, workshops and Posters Presentation on the latest treatment innovations in the field of Radiology, Oncology, Medical Imaging, and Cancer by experts from both Academic and Business background.
It also provides a premier interdisciplinary platform for researchers, practitioners and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns as well as practical challenges encountered and solutions adopted in the fields of Radiology and Oncology.
Radiology and Oncology 2018 committed to creating real and reliable contributions to the scientific community. Conference Series Ltd organize 2000+ Conferences once a year across the USA, Canada, Mexico Europe, Georgia, Middle East & Asia with support from a thousand additional scientific societies and Publishes 900+ Open access journals that contain over thousands eminent personalities, putative scientists as editorial board members.
Why attend??
Encounter the target market with members from across the globe, committed to learning about Radiology and Oncology. This is the best opportunity to outreach the largest gathering of participants from around the world. Conduct presentations, distribute and update knowledge about Radiology and Oncology and receive name recognition at this 2-days event. World-eminent speakers, most recent researches, latest treatment techniques and the advanced updates in Radiation Oncology are the principal features of this conference.
Target Audience:
Our Organization would be privileged to welcome them:
-
Directors of Radiology and Oncology or related Programs or Associations
-
Heads, Deans and Professors of Radiology and Oncology department
-
Radiology and oncology Doctors
-
Business Professionals
-
Radiographers and Radiology Technologists
-
Educators, Scientists, and Researchers
-
Research Scholar
-
Radiation Oncologists
-
Radiology Consultants
-
Lab Technicians
-
Healthcare professionals
-
Fellows
-
Residents
-
Founders and Employees of the related companies
-
Clinical investigators & Researcher
-
Hospitals and Health Services
-
Pharmaceutical companies
-
Laboratory members
-
Support organizers
-
Radiologist and Oncologists
Conference Sponsor and Exhibitor Opportunities
The Conference offers the opportunity to become a conference sponsor or exhibitor.
Highlights of latest advances on Radiology and Oncology 2018
Track 1: Pediatric oncology
Pediatric oncology is a healthy development in drug associated with diagnosing and treating kids, as a rule up to the age of 18, with malignancy. It is thought to be one of the most challenging of specialties because, despite favorable treatment of many children, there is a high death rate still connected with different sorts of malignancies. Sorts of Pediatric Oncology include Pediatric Hematology Oncology, Neuroblastoma in Children, Pediatric Leukemia, Clinical Trials, Advanced Pediatric Oncology Drugs, Brain Tumor in Children, Advances in Pediatric Oncology Treatment, Oncology Nursing and Care, Pediatric Oncology Diagnostic, Pediatric Radiation Oncology, Radiotherapy Oncology and Pediatric Neuro-Oncology.
-
Advancing our Understanding of Neuroblastoma
-
Innovative high-performance computing
-
Dell cloud technology
-
Harnessing the Immune System to Fight Cancer
-
Genomic Approaches to Drug Discovery
Track 2: Cancer & Therapeutics
The word Cancer originates from the Latin (initially Greek) determined term for crab, due to the way a malignancy clings to any part that it seizes upon in an unshakable way like the crab.
Another expression for disease is "threatening tumour." Tumour actually signifies "swelling" or "mass." For this situation, it alludes to a mass of non-organized new cells, which have no known reason in the physiological capacity of the body.
-
Carcinomas
-
Lymphomas
-
Leukaemias
-
Brain tumours
-
Sarcomas
Track 3: Radiology Trends and Technology
Radiology is the science that utilizations restorative imaging to analyse and here and there likewise treat maladies inside the body. An assortment of imaging systems, for example, X-ray, radiography, ultrasound, registered tomography (CT), atomic pharmaceutical including positron discharge tomography (PET), and attractive reverberation imaging (MRI) are utilized to analyse or potentially treat infections. Interventional radiology is the execution of (ordinarily negligibly intrusive) therapeutic methodology with the direction of imaging innovations.
The securing of restorative pictures is normally done by the radiographer, regularly known as a Radiologic Technologist. Contingent upon area, the Diagnostic Radiologist, or Reporting Radiographer, at that point translates or "peruses" the pictures and delivers a report of their discoveries and impression or conclusion.
-
Medical radiography
-
Radiation protection
-
Teleradiology
-
Fluoroscopy
-
Pediatric Radiology
-
Nephrostomy
-
Spinal Cord Embolisation (AVM/DAVF)
Track 4: Oncology
Oncology is the branch of therapeutic science managing tumors, including the birthplace, advancement, determination, and treatment of harmful neoplasms. It incorporates therapeutic oncology which uses chemotherapy, hormone treatment, and diverse prescriptions to treat malignancy,radiation oncology using radiation for treatment and surgical oncology.
-
Benign tumors
-
Malignant Tumors
-
Oncogene
-
Cell mutations
-
Metastasis
-
Apoptosis
Track 5: Neuroradiology and Neuro-oncology
Neuroradiology is the subdivision of radiology that deals with the sensory or nervous system. It is the subspecialty of radiology which is converging on the diagnosis and characterization of variations from the peripheral nervous system, spine, and head and neck utilizing neuroimaging strategies. X-rays is utilized as a part of the analysis and treatment of nervous system disorders. Essential imaging modalities incorporate Computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ultrasound and Plain radiography is used on a constrained premise and in limited conditions, individual in pediatric population.
Neuroradiology has a critical part to play in Diagnosis and Treatment of Several Neurological issue like Ischemic Stroke and the Structural injuries causing Cerebral Haemorrhage. The current advances are rising all the more quickly in the exploration fields of Neuroradiology incorporates the improvement of MR imaging of the Brain and Spinal cord neoplasms.
-
Clinical Neuroscience
-
Brain Morphometry
-
Multivariate Deposits In Brain Imaging
-
Radiation Technology in Neuroscience
-
Neurosonology
-
Spine Intervention
-
Clinical Neuroradiology
-
Central Nervous System Malignancies
-
Whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT)
Track 6: Anaesthesia
Anaesthesia is a method to control pain during a surgery or procedure by using medicine called anaesthetics. It can help control your breathing, blood pressure, blood flow, and heart rate and rhythm.
Anaesthesia may be used to:
-
Relax you.
-
Block pain.
-
Make you sleepy or forgetful.
-
Make you unconscious for your surgery.
Track 7: Cancer Cell Biology and Cancer Biomarker
The cell is the basic unit of life. It is the littlest structure of the body fit for playing out the majority of the procedures that characterize life.
Each of the organs in the body, for example, the lung, breast, colon, and brain, comprises of particular cells that complete the organ's capacities, for example, the transportation of oxygen, processing of supplements, proliferation, considering etc.
Cancer cells have defects in normal cellular functions that enable them to separate, attack the encompassing tissue, and spread by method for vascular as well as lymphatic systems. These defects are the consequence of quality transformations and mutation and there caused by irresistible infections.
Biomarkers have various potential applications in oncology, including hazard appraisal, screening, differential investigation, assurance of visualization, expectation of reaction to treatment, and monitoring of progression of disease.
-
Genomic instability
-
Oncogenes and protoncogenes
-
Tumor suppressor genes
-
Epigenetics
-
Cancer stem cells
-
Virology and Cancer
-
Molecular tumor biomarker
-
Risk evaluation
-
Prognosis and treatment forecast
Track 8: Cancer Therapies
Cancer Treatments are medical therapies that asserted to treat cancer by different methods like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation oncology, and immunotherapy. Oncolytic biotherapy is a rising treatment method of cancer which uses infections to destroy cancers. The recent development in genetic engineering techniques has been made using viruses to attack and destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy is a method of cancer treatment which uses chemical substances or chemotherapeutics drug to kill the cancerous cells.It is one of the major methods of medical oncology.
-
Surgery
-
Chemotherapy
-
Radiotherapy
-
Immunotherapy
-
Drug therapy, gene therapy
-
Cancer drug designing
-
Nanotechnology in Cancer drugs
Track 9: Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine is a medical specialty that utilizations radioactive tracers (radiopharmaceuticals) to distinguish substantial capacities and to analyse and treat infection. Nuclear medicine is a branch of radiology and therapeutic imaging. Unique way to kill malignancy cells with insignificant damage to encompassing tissue.
Nuclear medicine treatment utilizes larger amount of radiation to treat thyroid disease and tumour. It utilizes small amount of radioactive pharmaceuticals. This method help characterize diseases in practically every organ system including the heart, mind, skeleton, thyroid and kidneys and many type of tumour and can be utilized to treat illness without surgery. This is one of a unique approach to kill cancer cells with minimal damage to surrounding tissue.
Track 10: Radiation Oncology
Radiation oncology is one of the three basic specialties, the other two being surgical and therapeutic oncology, related with the treatment of development. Radiation can be given as a therapeutic system, either alone or in mix with surgery or possibly chemotherapy. The mission of Advances in Radiation Oncology is to give unique clinical research went for improving the lives of people living with tumour and distinctive ailments treated with radiation treatment.
-
Radiation Therapy
-
Predictive Oncology
-
Cancer Imaging
-
Stem Cell Therapy
-
Oncology Nursing
Track 11: Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
There are three types of treatment modalities accessible for treating disease Surgery, Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy. Surgical oncology is the branch of surgery connected to oncology. Surgical oncology utilizes surgical techniques to analyze, stage, and treat growth, and to treat certain cancer related side effects. Surgery assumes an essential part in the administration of both early tumors and additionally propelled diseases in blend with chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Surgical Oncology Sub-Specialties
-
Head and Neck Oncology
-
Breast Oncology
-
Gastrointestinal Oncology (Gastro Oesophageal , Hepatoma – Biliary, Colorectal diseases)
-
Thoracic Oncology
-
Genito-Urinary and Gynae Oncology
-
Bone and Soft Tissue Tumours
Track 12: Radiography
Medical radiography is a broad term that covers several types of studies that require the visualization of the internal parts of the body using x-ray techniques.
-
Angiography
-
Mamography
-
Digital radiography
-
Pediatric radiography
Track 13: Clinical Radiology
Clinical radiology is a specific branch of medicine that uses state of the art equipment and a range of techniques to capture images of the inside of the body.
Clinical radiologists use various imaging techniques including:
-
X-ray
-
Ultrasound
-
Computed tomography (CT) including multislice scanning
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
-
Positron emission tomography coupled with CT or MRI (PET-CT or PET-MRI) – enabling enhanced 3D images
-
Fluoroscopy – using real-time x-ray imaging to show internal structures of the body
-
Molecular imaging – CT perfusion, dual-energy CT, optical imaging
-
Nuclear medicine techniques
Track 14: Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a sort of imaging and part of radiology. It utilizes high-frequency sound waves to catch live images from inside your body. Ultrasound is protected and easy. Ultrasound is a valuable methodology for observing the child's improvement in the uterus.
-
Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging
-
Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging
-
Transabdominal
-
Obstetric Ultrasound Imaging
-
Medical ultrasonography
-
Ultrasound attenuation spectroscopy
Track 15: Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography- PET/CT
Positron-outflow tomography (PET) is an atomic medication utilitarian imaging strategy that is utilized to watch metabolic procedures in the body. The framework recognizes sets of gamma beams discharged in a roundabout way by a positron-transmitting radionuclide (tracer), which is brought into the body on a naturally dynamic atom. In present day PET-CT scanners, three-dimensional imaging is frequently refined with the guide of a CT X-beam filter performed on the patient amid a similar session, in a similar machine.
Computed tomography (CT), sometimes called "computerized tomography" or "computed axial tomography" (CAT), is a noninvasive medical examination or procedure that uses specialized X-ray equipment to produce cross-sectional images of the body.
CT is a valuable medical tool that can help a physician:
-
Diagnose disease, trauma or abnormality
-
Plan and guide interventional or therapeutic procedures
-
Cancer treatment
Track 16: Medical Imaging Technology
Medical imaging is the procedure used to make visual representations of the human body for clinical purposes or medicinal science (including the study of normal anatomy and physiology). Medical imaging technology plays an important role in health care system.
Imaging for therapeutic purposes includes a group which includes the administration of radiologists, radiographers (X-ray technologists), sonographers (ultrasound technologists), medicinal physicists, biomedical designers, and other support staff working together to optimize the wellbeing of patients, each one in turn. Appropriate utilization of medical imaging requires a multidisciplinary approach.
-
Thermography
-
Photoacoustic Imaging
-
Tactile imaging
-
Elastography
-
Ultrasound
-
Nuclear medicine
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
-
Modern Radiotherapy and Quality assurance
-
Molecular Imaging
-
X-ray imaging
-
Mammography
-
Endoscopy
Track 17: Head & Neck Radiology
Head and neck radiology, similar to that of other subspecialties in radiology. The head and neck refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal cord and their associated vascular structures and encasing membranes i.e. the meninges.
Track 18: Molecular Imaging Methodology
Molecular imaging methodology which are non-intrusive, Painless and safe. Molecular imaging is a type of medical imaging. Molecular Imaging is the visualization, characterization, and measurement of biological processes at the molecular and cellular levels in humans and other living systems. Where other analytic imaging techniques—such as x-rays, computed tomography (CT), MRI or magnetic resonance imaging, CT scan and ultrasound—offer pictures of physical structure, molecular imaging allows physicians to see how the body is functioning and to measure its chemical and biological processes.
At the point when are they utilized?
Molecular Imaging are utilized to analyse and diagnose the treatment of cancer, heart disease, brain disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, gastrointestinal disorders, lung disorders, bone disorders, kidney and thyroid disorders, and more.
-
Carcinomas
-
Lymphomas
-
Leukaemias
-
Brain tumours
-
Sarcomas
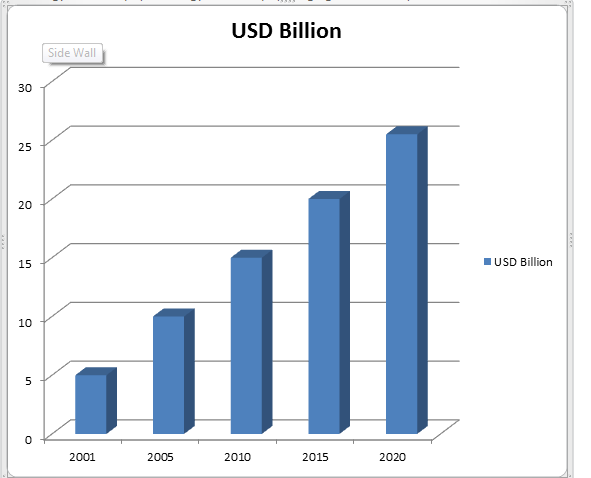
The Market Analysis Report of Radiology and Oncology is expected to reach USD 25.50 Billion by 2020 from USD 17.99 Billion in 2017. The market is broadly classified into product, procedure type, and application.
The product segment of the market is further divided into Radiography system, angiography systems, fluoroscopy systems, CT scanners, ultrasound-imaging systems, MRI systems, and other medical devices.
Radiology and Oncology markets continue to grow amid a more educated global population, increased awareness and advanced technology used for Disease diagnostics.
Market Analysis Report of Radiology and Oncology in USD Billion
The number of new cancer cases diagnosed every year is increased from 14.9 million of 2012 to 25.50 million by 2020. The expansion in new cases is because of a steadily aging population. Both developed and developing countries have maturing or growing population.
Innovation and technology enhances the accuracy and appropriateness of radiotherapy and radiosurgery. Large number uses of Radiotherapy and radiosurgery equipment’s occur because the units are able to treat a broader range of cases. Advances in equipment and programming are providing a business opportunity replacing an aging installed base. New designs and outlines can convey high standards of care.
The rise in cancer cases, together with the expansion in sophistication of new treatment etiquette, has made interest for more automated products. Automation relies upon incorporation of a few devices into clinically useful frameworks. Coordinated frameworks make medications quick and practical.
Innovation progresses prompt enhancements in patient care. The accessibility of advanced, mechanized and productive clinical apparatuses in radiation therapy has brought more exact types of radiotherapy treatment (IMRT, IGRT, VMAT, SRS, SBRT, brachytherapy and proton treatment). Innovation and Technology incorporates the EDGE™ and Truebeam™, and the Accuray TomoTherapy H Series and CyberKnife M6 stages that empower medications that diminish treatment times and increment persistent throughput .
Target Audience for this Report:
- Radiology and Oncology manufacturer and distributors
- Medical Institutions (Hospitals,Healthcares, Medical centers, Diagnostic centers Medical schools, Group practices, Individual surgeons, and Research labs) various research centers and consulting companies
Related Conferences
1. International Conference on Biomarkers and Cancer Targets , July 16-17, 2018 Dubai, UAE
2. Head and Neck Oncology Conference: Precaution and Treatment, August 30-31, 2018 Dubai, UAE
3. 8th World Conference on Women’s Health and Breast Cancer, August 09-10, 2018 Abu Dhabi, UAE
4. International Conference on Neurooncology and Neurosurgery , September 20-21, 2018 Dubai, UAE
5. 4th International Conference on Anaesthesia and Pain Medicine, September 17-18. 2018 Dubai, UAE
6. 3rd International Conference on Neuroradiology & Imaging June 01-02, 2018 Osaka, Japan
7. World Haematology and Medical Oncology Conference May 28-29, 2018 Osaka, Japan
8. 33rd International Conference on Oncology Nursing and Cancer Care September 17-18, 2018 Tokyo, Japan
9. 3rd Cancer Diagnostics Conference & Expo September 20-21, 2018 Berlin, Germany
10. 22nd Global Annual Oncologists Meeting, May 24-25, 2018 Osaka, Japan
11. Experts Meet On Cancer Therapy 2018, July 23-24, 2018 Melbourne, Australia
12. 28th Euro Congress on Cancer Science & Therapy Conference August 09-10, 2018 Madrid, Spain
13. 4th World Congress on Medical Imaging and Clinical Research Conference September 03-04, 2018 London, UK
14. 21st World Congress on Radiology , August 27-28, 2018 Toronto, Ontario, Canada
15. 12th International Conference on Abdominal Imaging and Endoscopy Conference, June 28-29, 2018 Amsterdam, Netherlands
16. 36th World Cancer Conference October 11-13, 2018 Zurich, Switzerland
17. 26thAnnual Congress on Cancer Science and Therapy Conference October 29-30, 2018 San Francisco, California, USA
18. Gastrointestinal Cancer and Therapeutics Conference October 29-30, 2018 San Francisco, USA
19. 17th Asian Oceanian Congress of Radiology, January 25-28, 2018, Mumbai, India
20. Pan Arab Interventional Radiology Society Annual Congress, February 21-24, 2018 Dubai, UAE
21. Cancer Imaging and Therapy Conference, April 2-6, 2018, Hollywood, United States
22. Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery Congress, June 20-23, 2018, Berlin, Germany
23. The 77th Annual Meeting of the Japan Radiological Society, April 12-15, 2018, Japan
24. Emergency Radiology Conference, January 19-21, 2018, Tucson, Arizona, USA,
25. Cardiac MRI Congress January 25-26, 2018, Cambridge, UK
26. Breast Ultrasound Conference, January 15-16, 2018, Houston, Texas, United States
27. Breast Imaging and Body MRI Conference, January 7-12, 2018, Kamuela, Hawaii 96743, United States
28. Duke Radiology in the Islands 2018, January 15-18, 2018, Palm Beach, Aruba
29. 5th World Congress and Expo on Oncology & Radiology, December 06-08, 2018 Valencia, Spain
30. 4th Global Radiology Education congress, February 8-10, 2018,Bali, Indonesia
Related Societies
Middle East
- Emirates Radiology Society
- Pan Arab Interventional Radiology Society
- Turkish Society of Radiology
- Middle East Cancer Consortium
- Arab Medical Association Against Cancer
USA
- Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
- American Board of Radiology
- Association of Educators in Imaging and Radiologic Sciences,
- The Association for Medical Imaging Management
- American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine
- American Society of Head and Neck Radiology
- American Society of Neuroradiology
- Canadian Association of Radiologists
- American College of Nuclear Medicine
- American Society of Clinical Oncology
- American Association for Cancer Research
- Society for Neuro-Oncology
- Mexican Association of Ultrasound in Medicine
- American Osteopathic College of Radiology
- American Society for Radiation Oncology
- American Cancer Society, American Society of Pediatric Haematology/Oncology
- Association of Community Cancer Centers, Musculoskeletal Tumour Society
- National Cancer Registrars Association
- Oncology Nursing Society
- Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer
- Long Island Radiological Society
Europe
- Italian Society of Medical Radiology
- European Society for Medical Oncology
- Argentinian Federation of Diagnostic Radiology and Radiation Therapy Associations
- European Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology
- European Society of Head and Neck Radiology
- European Society of Cardiac Radiology
- Eastern Radiological Society
- Computerized Medical Imaging Society
- Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe
- European Society of Musculoskeletal Radiology
- French Society of Radiology
- French Society of Nuclear Medicine
- Spanish Society of Nuclear Medicine
- Spanish Society of Vascular and Interventional Radiology
- Spanish Society of Radiology
- Nordic Society of Medical Radiology
- Norwegian Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging
- Swedish Society of Nuclear Medicine
- Swiss Society of Nuclear Medicine
- Swedish Society of Radiology
- British Nuclear Medicine Society
- Society of Radiologists in Training
- British Institute of Radiology
- British Society of Neuro radiologists
- British Society of Interventional Radiology
- Long Island Radiological Society
- Swiss Congress of Radiology
- Czech Radiological Society
- Czech Society of Nuclear Medicine
- Czech Society for Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography
- Society for Vascular Ultrasound
- European Society of Head and Neck Radiology
Asia-Pacific
- Hong Kong Anti-Cancer Society
- Society of Indian Radiographers
- Indian Cancer Society
- Korean Cancer Association
- Asian Clinical Oncology Society
- Japan Radiological Society
- Japan Society of Clinical Oncology
- Japan Radiological Society
- Japan Medical Imaging and Radiological Systems Industries Association
- Japanese Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- Japanese Society of Sonographers
- Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology
- Japanese Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology
- Japan Society for Molecular Imaging
- Society of Nuclear Medicine India
- Chinese Society of Nuclear Medicine
- International Society for Therapeutic Ultrasound
- Radiological Society of the Republic of China
- Asia Pacific Society of Cardiovascular & Interventional Radiology
- Hong Kong Society of Nuclear Medicine
- Korean Society of Radiology
Top Universities
Middle East
USA
Advancements in Ultrasound in Radiology: Radiology & Oncology 2018
Sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing are termed as Ultrasound. It is no different from audible sound in its dynamic characteristics, besides in that individuals cannot listen to it. This boundary modifies from person to person and is roughly 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy, young adults. Ultrasound devices work with pulses from 20 kHz up to various gigahertz.
A new survey of radiology professionals discovered that ‘image quality’ and the ‘right balance of price versus performance’ were the most influential parts when adopting a unique ultrasound system. Advanced innovations and trademark name were classified least important, according to the results from the report.
Working in partnership with several leading equipment manufacturers, a new questionnaire was designed to gather feedback from radiologists using ultrasound imaging equipment.
The results highlighted the increasing pressure radiologists are under due to declining reimbursement rates in all over the world. Radiologists are searching for fewer costly ultrasound systems that can operate increased testing standards, but without spending increased amounts. Other highlighted trends in the reports include the real impact of developed visualization software for reliable and more effective ultrasound-guided methods.
Doctor’s judgments were collected on the devices they were accepting, and the experiments conducted. Views on system enhancements and effect on work-flow, projected expectations for movable and hand-carried systems, training and after-sales assistance were also inquired, as well as factors controlling acquiring decisions.
Radiotherapy-resistant tumors could be defeated with experimental drugs
Radiotherapy-resistant tumors could be beaten with innovative medications. Individualized cancer therapy has been a crucial idea since the source of cancer study. Nearly 70% of cases undergo radiotherapy as part of their therapy, which is one of the most cost-effective cancer medications. Distinctly, around 50% of cancer remedies include the use of radiotherapy, either as a single modality or coupled with other practices.
Radiotherapy can provide a huge benefit to sufferers of cancer. In the past decade, important technical improvements, such as image-guided radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy, medical imaging technology, biological therapy, and chemotherapy and proton therapy enable higher doses of radiotherapy to be delivered to a tumor with significantly deeper doses to normal enclosing tissues.
It may be possible to use drugs that are already an improvement to overcome radiotherapy revolution in tumors, which is often a major barrier to the successful treatment of many cancers.
Radiation therapy shrinks tumors by directing X-rays, gamma rays, or charged particles at them. These high-energy beams — which can come from a machine outside the body or from radioactive materials implanted into the body — kill the cancer cells by destroying their DNA.
Radiation and Chemical Treatment which are affecting in Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases with more than 100 different types each with their own set of risk factors. The risk of developing cancer increases with age, differences in gender, race and personal and family medical history. Most risk factors are largely related to lifestyle choices occupational exposures and some environmental factors help in developing cancer.
The factors which contribute to cancer include physical factors, genetic factors, epigenetic factors, biological factors and lifestyle factors which lead to tumor formation. Some of the risk factors for different types of cancer are described below:
Physical Factors:
Physical factors include Radiation and Chemical factors.
Radiation:
10% of total cancer cases are induced by radiation, both ionizing and nonionizing, mainly from radioactive substances, ultraviolet (UV) rays and pulsed electromagnetic fields. Cancers induced by radiation include leukemia, lymphoma, thyroid cancer, skin cancer, sarcomas, lung and breast carcinomas. Ex: Increased risk of cancer after exposure to radiation causes total malignancies observed in Sweden after exposure to radioactive substances from the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. Exposure to radiations like x-rays used in medical settings for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The risk of breast cancer from x-rays mostly seen in girls exposed to chest irradiation at puberty.
Nonionizing radiation from sunlight like UV rays is carcinogenic to humans which cause skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. Depletion of the ozone layer in the stratosphere can augment the dose-intensity of UVB and UVC, which causes skin cancer (Belpomme, 2007)
Chemical and Environmental Factors which cause Cancer:
Some of the chemicals which cause cancer are nitrates, dioxane, pesticides, poly-aromatic hydrocarbon, nitric oxide, chlorinated drinking water, indoor air-pollutants etc.. Nitrates and Chlorinated drinking water contribute to colorectal, bladder, leukemia and lymphoma cancer. The food which contains radioactive nuclei like radium, uranium causes gastric cancer. Pesticides which are used in agriculture cause leukemia, lymphoma, brain tumors, Wilm’s tumors, Ewing’s sarcoma and germ cell tumors.
Children's (Pediatric) CT (Computed Tomography)
Radiology and Oncology 2018 today announced an important milestone in computed tomography (CT) scanning for the center in Dubai.
Pediatric computed tomography (CT) is a fast, painless diagnostic Process that uses special X-ray tools to produce complete photographs of your child’s blood vessels, bones, soft tissues and internal organs. It may be used to help diagnose abdominal pain or evaluate injury after trauma.
What is Children's CT?
Most commonly known as a CT or CAT scan, is an indicative therapeutic test that, like conventional X-rays, generates multiple images or pictures of the core of the body.
The cross-sectional illustrations produced during a CT scan can be reformatted in various planes, and can even produce three-dimensional images. These photographs can be observed on a computer monitor, printed on film or transferred to a CD or DVD.
CT pictures of internal organs, delicate tissue and veins give more prominent part than regular X-rays, particularly of blood vessels acnes.
CT scan might be directed on babies, new-born children and young people.
Some common uses of the system
- CT is utilized to help analyze a wide assortment of circumstances because of torment or weakness.
- CT may also be performed to evaluate blood vessels throughout the body.
- CT is the most commonly used imaging method for evaluating the chest
- It is used to obtain very detailed pictures of the heart and blood vessels in children, even newborn infants.
- CT is well-suited for imaging diseases or impairment of vital organs in the stomach including the kidney, spleen and the liver.
- CT scans can help in detect sores or tumors in the pelvis and assess for masses in the urinary region
- CT is an added example of new medical technology to help doctors specifically to diagnose disease. Patients with heart disease require specific diagnoses, and they frequently want them quick.
NIR light may identify breast cancer patients who will benefit most from chemotherapy
A new optical imaging system developed to recognize bosom disease patients who will react to chemotherapy. The imaging framework might have the capacity to foresee reaction to chemotherapy as right on time as two weeks after starting treatment.
New imaging frameworks - a noninvasive strategy for estimating bloodstream progression because of a solitary breath hold - were distributed today in Radiology and Oncology 2018. There is as of now no technique that can foresee treatment result of chemotherapy at an early stage in treatment, so this is a noteworthy progress. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, given for five to a half year before surgery, is the standard treatment for a few ladies with recently analyzed obtrusive, however operable, bosom growth. The point of neoadjuvant chemotherapy is to dispense with dynamic tumor cells - delivering an entire reaction - before surgery. The individuals who accomplish a total reaction have a lower danger of malignancy repeat than the individuals who don't. Notwithstanding, less than half of ladies treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy accomplish a total reaction.
Specialists are additionally considering other imaging advancements for bosom disease treatment checking, for example, MRI, X-beam imaging, and ultrasound.
X-ray imaging utilizes harming radiation as isn't appropriate for treatment observing, which requires imaging sessions each half a month," he says. "X-rays are costly and take quite a while, from 30-a hour and a half, to perform. Since our framework takes pictures in under 10 minutes and utilizations innocuous light, it can be performed more every now and again than MRI.
Higher doses of radiation don't improve survival in prostate cancer
A newer investigation demonstrates that higher doses of radiation do not enhance endurance for some patients with the prostate disorder, compared with the standard radiation treatment.
Past investigations have demonstrated that gradually increasing the radiation measurement brought about enhanced malignancy control, for example, slower tumor development and lower levels of prostate-particular antigen (PSA), a pointer to disease development.
"We will likely enhance survival, however, we didn't see that regardless of advances in current radiotherapy," The investigation included around 1,500 patients with transitional hazard prostate tumor, the hazard classification in which most patients fall. Through the span of the investigation, 51 patients kicked the bucket of prostate growth, which is 3.4 percent of all patients selected.
In the event that we can securely convey the higher dosage of radiation, it shows a lower risk of recurrence, which brings about better personal satisfaction. However, in the event that we can't accomplish those 'sheltered' radiation dosage objectives, we shouldn't put the patient in danger of genuine symptoms down the line by giving the higher measurements. In the event that we can't spare the rectum or the bladder all around ok, for instance, we ought to most likely back off the radiation dosage. It's critical to create treatment gets ready for every patient on a case-by-case premise."
This work was upheld by 2nd World Congress on Radiology and Oncology during July 16-17, 2018 to be held at Dubai, UAE. Radiology and Oncology 2018 is a 2-day event offering wider sessions involving Keynote presentation, Oral, YRF (student presentation), poster, e-poster presentations. visit: https://radiology-oncology.annualcongress.com/
New anti-cancer protein discovered
A worldwide association of scientists has found a novel hostile to malignancy protein. The protein, called LHPP, frustrates the broad proliferation of disease cells in the liver.
The frequency of liver malignancy, additionally delegated hepatocellular carcinoma, is always advancing. In the previous decade, the abundance of cases has altogether brought up in everywhere throughout the globe.
Liver tumors stretch out from changed cells that develop and engender wildly. Hostile to malignancy proteins, supposed tumor silencers, restrain boundless cell development. Tumor silencers are regularly insufficient in disease cells
In the examination, the reason that the loss of LHPP empowers blister development and abatements the likelihood of the steadiness of disease patients. LHPP could attainably be utilized as a prognostic biomarker. LHPP is beneficial as a biomarker to stratify tumors.
Phosphorylation necessary for tumorigenesis
LHPP is a phosphatase that separates histidine-linked phosphate groups from proteins. Similar to all amino acids, histidine is a basic element of proteins. Histidine phosphorylation of proteins has been inadequately reviewed due to the absence of suitable tools.
Due to the lack of LHPP, global protein histidine phosphorylation is improved, which can transport into activation of various fundamental functions and independent cell generation. This lack promotes the growth of tumors by raising histidine-phosphorylated proteins. The tumor suppressor LHPP may also perform an important role in the growth of other cancers.
Gene Therapy: Applications in Interventional Radiology
Gene therapy is a unique and rapidly advancing sector of medicine. Gene therapy is an impressive frontier in medicine now.
Although it is a new therapy technique, recent studies seem encouraging. Because the vascular wall is an immeasurable target for this method, interventional radiologists should grow to progress with this innovative therapy and be affected by this multidisciplinary collaboration.
New imaging methods represent an opportunity to recognize and determine vascular gene therapy. Radiologists play an important role not only in developing and mastering endovascular genetic invasions but also in evaluating the progress of vascular gene therapy and reading further cultivation of vascular gene therapy technology.
Gene therapy in a droplet could heal eye disease and disorders, prevent blindness
Eye disorder such as diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration are with the leading problems of irreversible vision loss and blindness universal.
Currently, gene therapy can be administered to review these situations -- but this needs an injection. Now researchers report a new way to deliver the medication topically, instead of a needle. The rear portion of the eye is where infirmities such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration occur. And they require a substance called vascular endothelial growth factor, which excites the growth of blood vessels. Specialists must be working to inhibit the growth factor working on gene therapy technique, but delivering drugs to the back of the eye currently needs an injection. The researchers received a gene delivery method with a peptide called penetration, which has shown excellent permeability in the eye, and a polymerized polymer called poly (amidoamine) that has previously been used in drug delivery. The conclusions show that the method's potential for delivering gene therapy to treat several eye diseases and mutation.
Hot Tea Linked to Esophageal Cancer Risk
Tea lovers who take their warm Tea normal are elevating their threat of having esophageal cancer if additionally, they drink alcohol each day or if they smoke, say researchers. A study that includes more than 450,000 people in China for nine years, offering proof that the connection between consuming hot tea every day, regular drinking and smoking are having a higher risk of esophageal cancer.
The possibility of cancer has been increased in the individuals who use in drinking hot tea every day and smoked tobacco, analyzed among nonsmokers who took tea hardly occasionally. Conclusions suggest that risk of esophageal cancer related to the merger of high-temperature tea drinking, and using of alcohol, and smoking.
In less developed countries particularly in men, this esophageal cancer is increasing rapidly. In China, where the rate of esophageal cancer is among the highest in the world, men who drink tea often smoke and drink alcohol.
The study included 456,155 participants age group of 30 to 79 years who did not have a history of cancer. All were enrolled between 2004 and 2008 from five urban and five rural regions of China. At the start of the study, participants have taken the tea with the same temperature usually they take and also some of their other behaviors, including drinking alcohol and smoking. After 9 years, researchers found 1731 cases of esophageal cancer reported in 1,106 men and 625 women.
Cancer can be caused by obesity but Aspirin may prevent it- a new perception of potential targets for cancer prevention. Cancers like colon, pancreatic and breast cancer can be caused by Obesity. Studies have shown its role in regulating tumor growth and malignant progression. but for cancer initiation its role is uncertain.
"Epithelial defense against cancer" mechanism is the Epithelial cells which are at the surface of organs have the ability to remove malignant cells from their midst. Normally cell competition is a process by which cells sense harmful cells and push them out.
Researchers and their collaborators designed a mutant protein called Ras. Epithelial cells to know how obesity affects this defense Mechanism
Severe obesity is resulted by feeding the Ras mice high-fat diets and they suppressed the defense mechanism and thereby increased the Ras-transformed cells left in the tissue. This suppression has only seen in intestine and pancreas, but not in lungs. Later months the tumor was developed in the pancreas and supported past correlations between the intestine and pancreatic cancer, but not in lung cancer
The suppression of the defense Mechanism can cause fatty acids and chronic inflammation is observed by an experiment using mice model
Defense mechanism was enhanced when mice fed a high-fat diet and treated with aspirin which is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. this indicates that reinforcing the defense mechanism with aspirin could be utilized for prevention of cancer.
This the first report to show that the relation between normal cells and transformed cells are influenced by obesity and inflammation. It implies that cell competition can also affect factors such as infection, smoking, sleeping factors and aging.
3D images of cancer cells in the body
Scientists have explained an innovative method that can perform detailed three-dimensional images of the body's inside. This can be applied to study the development of carcinoma cells in the body.
Specialists and clinicians are in want of a better knowledge and understanding of carcinoma cells and their characteristics in series to produce targeted cancer medication. Individual cancer cells are often studied in test tubes before the studies have experimented in living organisms. "Our purpose is to visualize carcinoma cells inside the living body for detection their function, spread growth and how they respond to new and different therapies.”
This process is also known as photoacoustic imaging, that uses ultrasound waves produced by laser beams to create high-resolution, three-dimensional images of the body's insides. The major difficulty is that tumor cells are transparent. This performs it difficult to utilize optical techniques to analyze tumors in the bodyThe specialists found a specific gene into the genome of the carcinoma cells. Once, the gene originates a phytochrome protein inside the cells which produced from plants and bacteria. It works as a light sensor.
In the second step, the researchers illuminate the tissue with sharp beats of light at two distinct wavelengths using a laser. Inside the body, the light pulses are absorbed and converted into ultrasonic waves. Those waves, we can easily measure outside the organism and two images of the body's insides can be reproduced based on this data. This method is used for the examination of cellular and genetic processes in the living organisms.
The virtual brain could aid surgical planning
Researchers have invented neural activity based on the different anatomical structure of individual brain tumor sufferers using a stage described as "The Virtual Brain". The Initial step toward generating personalized brain models that could be worked to divine the consequences of tumors and the following surgery on brain function.
Brain surgery is sensitive work that needs to be careful preparation to maximally eliminate a tumor while transmitting the surrounding tissue intact. General procedures such as functional magnetic resonance imaging are utilized to map out a surgical procedure by identifying major functional areas nearby to the tumor. These strategies are limited.
However, in their capacity to predict the post-surgical consequence because of the complicated dynamics of the brain and the extensive and widespread variations of brain action.
Utilizing the open-source software (The Virtual Brain), researchers showed that these individualized models can perfectly divine the outcomes of the tumors on brain connectivity. This effect presents the chance of combining neuroimaging data with virtual brain modeling to enhance surgical preparation and outlines.
Launch switch for the most common pediatric malignant brain tumor
A delicate foundation for brain development could have significant middle people for the understanding and treatment of medulloblastoma, malignant brain tumor usually influencing youngsters. Sonic Hedgehog subtype medulloblastoma can occur at any age but is most commonly seen in children. When not fatal, the disease is characterized by severe neurocognitive impairments. Medulloblastomas come from the cerebellum, an area at the base of the skull that regulates motor control, posture, and balance. The Sonic Hedgehog subtype of medulloblastoma occurs when too much of a particular type of brain cells - the granule cells - are made. Granular cells make up the bulk of the cerebellum and make up 80% of all brain neurons. During normal development, many granule cells are produced when other neighboring cells release the Sonic Hedgehog protein. Be that as it may, some granular cells are made in the cerebellum even before the release of Sonic Hedgehog, which has impacted the specialists to analyze different conditions that control the beginning production of granular cells. This symbolizes Gpr161 functions as a tumor suppressor for Sonic Hedgehog medulloblastomas by blocking excessively many granule cells from being made. The granular cell behaves like a car on a downhill slope with the parking brake. The loss of the handbrake is as damaging as the throttle is pressed too hard.
In the Previous year, an audit of the National Cancer Database took after 6,000 cases with medulloblastomas. Certain, 1,700 were period 16 or more youthful and taken chemotherapy and radiation treatment.
This determines that Gpr161 functions as a tumor suppressor for Sonic Hedgehog medulloblastomas by blocking too several granule cells from being made.
Fragile X imaging study reveals differences in infant's brains
Children or babies during the neurodevelopmental, use MRIs technique to determine fragile X syndrome had less-developed white material compared to infants that did not generate the condition. Imaging several regions of white matter from various angles can help researchers converge on the underlying brain systems necessary for proper neuron connection.
This's our concern that beginning investigation and mediation will support kids with fragile X and their family.
One of the trials has been recognizing great way consequence tests or biomarkers that represent a response to intervention.
Fragile X syndrome is a genetic disorder and the common inherited problem of intellectual disability in males. Demonstrations include studious inabilities, problems with human interaction, suspended discourse, hyperactivity, uniform practices and discussion. Throughout 20 % of individuals with fragile X encounter seizures. About one-fourth of people with fragile X meet the characteristic tests for autism spectrum disease.
Think of bundles of cables arranged over the brain. Certain bundles of axons combine several elements of the brain so that neurons can swiftly interact with each other. This statement is crucial, particularly for conventional neurodevelopment during childhood.
Diseases in which Radiology is Helpful :
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA): Doctor can confirm the presence of an AAA with an abdominal ultrasound, abdominal and pelvic CT or angiography.
Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding: Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding occurs between menstrual periods, after sex, or after menopause. Specialist will probably perform a physical and pelvic exam and may test your blood, hormone levels and thyroid capacity to decide whether you are pregnant or transmit infection diseases. Imaging tests, for example, pelvic ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound, ultrasound of the uterus, pelvic MRI, hysteroscopy or endometrial biopsy likewise might be used to help diagnose your condition.
Alzheimer's Disease: Doctor will probably give advice total medicinal exam, including neurological, blood and mind imaging exams, for example, CT, MRI or PET/CT of the head.
Anal Cancer: Anal cancer, otherwise called anal carcinoma, is cancer of the anus. To help analyze this condition, your specialist will play out an advanced rectal exam and endoscopy. A MRI, CT, PET/CT, or an endoanal ultrasound may likewise be requested by your specialist.
Anaemia: Doctor will probably perform blood tests to analyze your condition. Specialist may prescribe chest X-ray, general ultrasound, CT scan and pelvis or body MRI to help find underlying conditions.
Angina Pectoris: Doctor may perform an electrocardiogram (ECG), an stress test without imaging or blood tests to help analyze your condition. Moreover, chest X-ray, chest CT, coronary CT angiography, heart MRI, coronary angiography, echocardiogram or stress test with imaging might be performed.
Appendicitis: Doctor may utilize abdominal or pelvic ultrasound, CT of the abdomen and pelvis, MRI of the pelvis or X-ray to evaluate your condition.
Arthritis: Doctor will probably lead a total physical and may perform blood tests to search for aggravation to help diagnose your condition. Additional tests may include bone X-ray, CT, MRI, sonography or ultrasound.
Blood Clots: Doctor will probably perform a physical examination, and you may undergo a venous ultrasound or a CT scan , abdomen/pelvis or head to help analyse your condition.
Breast Cancer: Doctor will probably advice a physical examination to assess a breast lump. To determine, your doctor may order mammography, breast ultrasound, breast MRI, PET/CT or scintimammography.
Carotid Artery Stenosis: Doctor may use carotid ultrasound, CT angiography (CTA), magnetic resonance angiography , or cerebral angiography to determine the presence and location of stenosis.
Cervical Cancer: Doctor may perform carotid ultrasound, CT angiography (CTA), magnetic resonance angiography , or cerebral angiography to determine the presence and location of stenosis.
Cholecystitis: Doctor may perform abdominal ultrasound, abdominal CT magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography or hepatobiliary nuclear imaging to help analyse your condition.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Doctor may perform pulmonary function testing (spirometry) or blood vessel blood gas examination to help analyse your condition. Chest X-ray or chest CT might be utilized to measure the extent of your disease.
Cirrhosis of the Liver: Doctor may perform MRCP or other abdominal imaging exams using CT, ultrasound or MRI to help analyze your condition. To confirm the diagnosis, biopsy, liver function tests or surgery may be performed.
Colorectal Cancer: Doctor may perform a colonoscopy, CT colonography (otherwise called virtual colonoscopy) or an an air-contrast barium enema to help analyze your condition.
Crohn's Disease: Doctor will probably carry out a physical exam to assess your condition and utilize blood and stool tests to to look for signs of bleeding and rule out other underlying causes, such as infection. You may also undergo flexible sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy, body CT, body MRI, MR enterography, upper GI, small bowel follow-through, or lower GI to confirm a diagnosis.
Cystic Fibrosis: Doctor will probably perform blood tests and may test your sweat for high salt substance, signal cystic fibrosis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, your specialist may assess your condition with a chest X ray, CT scan of the chest or abdomen, MRI of the chest or abdomen, abdominal ultrasound or CT of the sinuses.
Dense Breasts: There is no clear evidence that reducing breast density will reduce your risk of breast cancer. Communicate with your doctor about breast density and discuss what impact that may have on your breast cancer screening regimen.
Diffuse Interstitial Lung Disease: Blood tests, pulmonary function tests (spirometry), pulse oximetry, chest X-ray, chest CT, bronchoscopy with biopsy, or surgical biopsy might be performed to help analyze your condition.
Endometrial Cancer: specialist will probably carry out a physical exam to assess your condition. If endometrial cancer is suspected, your specialist may arrange a pap test, ultrasound of the uterus, or a biopsy.
Epilepsy: Doctor may direct a physical exam, electroencephalogram (EEG), head CT, head MRI or lumbar cut to help analyze your condition. Treatment options – including medicine and surgery – depend on the underlying cause.
Top Hospitals
UK
Radiology and Oncology 2017
Thanks to all of our speakers, conference attendees of Radiology and Oncology 2017 Conference were our best ever!
World Congress on Radiology and Oncology was held during October 19-20, 2017 New York, USA with the theme “Advancing Radiology in the multidisciplinary management of Oncology”. Benevolent response and active participation from the Scientists, Doctors, Professors, Researchers, Students, Pharmaceutical Industries and Healthcare Industries from the fields of radiology and oncology who made this event successful.
The meeting was carried out through various sessions, in which the discussions were held on the following major scientific tracks: Radiology Trends and Technology, Cancer Cell Biology and Cancer Biomarkers, Imaging Technology, Methodology and Software, Novel Approaches to Cancer Therapeutics, Oncology and its Major Field, Ultrasound and Mammography, Oncology Nursing, Radiation Oncology, Surgical Oncology, Neuro-Oncology, Neuro-Radiology and Radiotherapy, Cancer Pharmacology, Anti-cancer delivery, Medical Imaging and Diagnosis, Cancer Therapies, Breast Cancer and related Aspects, Radiology and Nuclear Medicine, Computer Assisted Tomography, Molecular Imaging, Advances in Cancer Imaging and Diagnosis, Head and Neck Radiology, PET/CT Scan | X Ray, Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Radiology and Oncology 2017 Organizing Committee would like to thank the Moderators of the conference – Dr. Janet Cordero, New York City College of Technology, USA.
The conference was initiated with a warm welcome note from Honourable guests and the Keynote forum lead by Dr. Zang-Hee Cho from Neuroscience Research Institute University of Suwon, South Korea and Dr. Arvind K. Chaturvedi from Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Institute & Research Centre, India and Dr. Wassil Nowicky from Ukrainian Anti-Cancer Institute, Austria and Dr. Yoshiaki Omura from New York Medical College,USA.
The highlights of the meeting were the eponymous lectures, delivered by:
- Dr. Alex Dommann, Empa-Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science and Technology, Switzerland
- Dr. Britt-Isabelle Berg, University Hospital Basel, Switzerland Dr. Dawn McDonald, James Paget Hospital, UK
- Dr. Nick Kostovic, Kostovic Acupuncture by bio Electron’s Laser, Corp., USA
- Dr. Slobodan Marinković, Belgrade University, Serbia
- Dr. Zoya Vinokur, New York City College of Technology, USA
- Dr. Anna Ćwierz, Ludwik Rydygier Memorial Specialized Hospital, Poland
- Dr. Lynette Watts, Midwestern State University, USA
- Dr. Ren Chongxi, Hebei Medical University, China
- Dr. Goanyup Lee, Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute, Korea
- Dr. Paweł Basta, Jagiellonian University, Poland
- Dr. Melosa D'souza, Royal Oldham Hospital, England
- Dr. Ahmad A. El Daba, Tanta University, Egypt
- Dr. Shajeem Shahudeen, Vivid Diagnostic Centre, India
- Dr. Aminur Rahman, National Institute of Neurosciences and Hospital, Bangladesh
- Dr. Akshay Kapila, Rajiv Gandhi Cancer Hospital, India
Panel Discussion
We are also obliged to various delegate experts, company representatives and other eminent personalities who supported the conference by facilitating active discussion forums at Radiology and Oncology 2017. We sincerely thank the Organizing Committee Members, Editorial Board Members of International Journals, Participants, Attendees and Media Partners for their gracious presence and generous support, without which the conference would not have reached the pinnacle of success. With the unique feedback from the conference, we would like to announce the commencement of the 2nd World Congress on Radiology and Oncology during July 16-17, 2018 at Dubai, UAE.
Let us meet again at Dubai, UAE.
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN USA
-
Nottingham University Hospitals NHS
-
Royal Cornwall Hospitals Trust
-
Leicester's Hospitals
-
Cumbria Partnership NHS Foundation Trust
-
Oxford University Hospitals Wrightington Wigan and Leigh
-
North East London Mental Health
-
Great Ormond Street Hospital
-
Heart of England NHS Foundation Trust|University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust
-
Christie Hospital NHS
-
Sheffield Teaching Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
-
Newcastle Upon Tyne Hospitals NHS
-
Royal Liverpool University Hospital
-
University Hospital Birmingham
-
Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust
-
Chelsea and Westminster Hospital
-
University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
-
Sandwell And West Birmingham Hospital Swbh NHS
-
Shrewsbury & Telford Hospital King's College Hospital NHS Foundation Trust
-
British Institute of Radiology
-
Harvard University
-
Stanford University
-
University of California
-
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
-
Michigan State University
-
Duke University
-
Yale University
-
Columbia University
-
Texas A&M University
-
The University of Texas
-
The University of Texas at Austin
-
Cornell University
-
New York University
-
Pennsylvania State University
-
Purdue University
-
University of Central Florida
-
University of Pennsylvania
-
University of Notre Dame
-
Northwestern University
-
University of Florida
-
The Ohio State University
-
University of Washington
-
Princeton University
-
Clemson University
-
University of Georgia
-
Florida State University
-
Georgetown University
-
University of Phoenix
-
Vanderbilt University
-
The University of Chicago
-
University of South Florida
-
University of Minnesota
-
University of Arizona
-
University of Maryland
-
University of Miami
-
California State University
-
Temple University
-
The University of Oklahoma
-
The University of Alabama
-
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
-
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
-
Mayo Clinic
-
Johns Hopkins Hospital
-
Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary
-
Massachusetts General Hospital
-
Mount Sinai Hospital
-
NHS Greater Glasgow and Clyd
-
Institute of Cancer Research Royal Cancer Hospital
-
BMI Health Care
-
Royal Marsden Hospital
-
Nuffield Health Hospitals
-
Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation
-
Trust|North Bristol NHS
-
Royal United Hospital NHS Trust
-
NHS LothianCentral Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
-
NHS Wirral Health Service
-
University Hospital Southampton NHS
-
South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust.
-
Hospital King's Lynn NHS Trust
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN EUROPE
-
University of Oxford
-
University of Cambridge
-
Imperial College London
-
KU Leuven World University
-
The University of Edinburgh
-
Ludwig Maximilians University
-
Technical University of Munich
-
University of Copenhagen
-
King's College London
-
The University of Manchester
-
University of Amsterdam
-
Delft University of Technology
-
Humboldt University of Berlin
-
KTH Royal Institute of Technology
-
University of Bologna
-
Heidelberg University
-
Anderson Cancer Center
-
Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center
-
Johns Hopkins Hospital
-
Medical University of Innsbruck
-
Johannes Kepler University Linz
-
Paracelsus Medical University
-
Medical University of Graz
-
Belarusian State Medical University
-
Gomel State Medical University
-
Grodno State Medical University
-
Université Catholique de Louvain
-
Université Libre de Bruxelles
-
Université de Liège
-
Universiteit Antwerpen
-
Universiteit Gent
-
Universiteit Hasselt
-
Universiteit Hasselt
-
Vrije Universiteit Brussel
-
Faculty of Medicine, University of Banja Luka
-
Faculty of Medicine, University of East Sarajevo
-
Faculty of Medicine, University of Sarajevo
-
Faculty of Medicine, University of Tuzla
-
International University of Goražde
-
Medical University Pleven
-
Medical University of Plovdiv
-
Medical University of Varna
-
Trakia University
-
University of Osijek
-
University of Rijeka
-
School of Medicine, University of Zagreb
-
University of Cyprus
-
European University Cyprus
-
Charles University
-
Masaryk University
-
University of Ostrava, Faculty of Medicine
-
Aalborg University
-
Aarhus University
-
University of Copenhagen Faculty of Health and Medical Sciences
-
University of Southern Denmark
-
University of Tartu
-
University of Eastern Finland
-
University of Helsinki
-
University of Oulu
-
University of Tampere
-
Aix-Marseille University
-
University of Angers
-
Victor Segalen Bordeaux 2 University
-
University of Western Brittany
-
University of Caen Lower Normandy
-
University of Franche-Comté
-
Université Lille Nord de France – Campus Lille II
-
University of Limoges
-
Claude Bernard University Lyon 1
-
Jean Monnet University
-
University of Montpellier 1
-
Henri Poincaré University
-
University of Nantes
-
Paris Diderot University
-
University of Reims Champagne-Ardenne
-
University of Poitiers
-
Petre Shotadze Tbilisi Medical Academy
-
Albert Ludwig University of Freiburg
-
Heidelberg-Mannheim
-
Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg
-
Eberhard Karl University of Tübingen
-
University of Ulm
-
University of Regensburg
-
Humboldt University of Berlin
-
Universitätsklinikum Benjamin Franklin
-
Heinrich-Heine University of Düsseldorf
-
Witten/Herdecke University
-
University of Athens
-
University of Crete
-
University of Patras
-
University of Thessaloniki
-
University of Thrace
-
University of Debrecen
-
University of Pécs
-
Albert Szent-Györgyi Medical University, Szeged
-
University of Iceland
-
National University of Ireland, Galway
-
Trinity College Dublin
-
University College Dublin
-
University of Limerick
-
University of Bari
-
University of Bologna
-
University of Parma
-
University of Rome La Sapienza
-
University of Catania
-
University of Malta
-
Universiteit van Amsterdam
-
VU University Medical Center Amsterdam
-
University of Groningen, Faculty of Medicine
-
Universiteit Utrecht
-
Norwegian University of Science and Technology
-
University of Oslo
-
University of Tromsø
-
Jagiellonian University Medical College
-
Medical University of Białystok
-
Medical University of Silesia in Katowice
-
Medical University of Lublin
-
Medical University of Åódź
-
Poznań University of Medical Sciences
-
Universidade Nova de Lisboa
-
University of Beira Interior
-
University of Lisbon
-
University of Porto
-
University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Grigore T. Popa"
-
University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Carol Davila"
-
Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy
-
Constanța
-
First Pavlov State Medical University of St. Peterburg
-
St. Petersburg State University
-
University of Belgrade School of Medicine
-
Comenius University
-
University of Novi Sad
-
Slovak Medical University
-
University of Ljubljana
-
Universidad de Alcalá
-
Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona
-
Universidad de Castilla-La Mancha
-
Universidad CEU Cardenal Herrera
-
Universidad de Extremadura
-
Universidad de Granada
-
Universidad de Murcia
-
Universidad de Navarra
-
Gothenburg University
-
Lund University
-
Umeå University
-
Linköping University
-
University of Basel
-
University of Geneva
-
University of Fribourg
-
University of Lausanne
-
Abant Izzet Baysal University
-
Adnan Menderes University
-
Akdeniz Üniversitesi
-
Atatürk University
-
BaÅŸkent University
-
Bülent Ecevit University
-
Çukurova Üniversitesi
-
Dumlupınar University
-
Kırıkkale University
-
Gazi Üniversitesi
-
Maltepe University
-
Uzhhorod National University
-
Kyiv Medical University
-
O.O. Bogomolets National Medical University
-
Brighton and Sussex Medical School
-
Bristol Medical School
-
Durham University School of Medicine and Health
-
Imperial College School of Medicine
-
King's College London School of Medicine and Dentistry
-
Lancaster Medical School
-
Leeds School of Medicine
-
Liverpool Medical School
-
Manchester Medical School
-
Medical Sciences Division, University of Oxford
-
St George's, University of London
-
University of Birmingham Medical School
-
Southampton Medical School
-
Warwick Medical School
-
Southampton Medical School
-
Sheffield Medical School
-
Cardiff University School of Medicine
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN MIDDLE EAST
-
Arabian Gulf University
-
Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland - Bahrain
-
Kasr El-Aini Faculty of Medicine
-
Alexandria Faculty of Medicine
-
Faculty of Medicine Zagazig University
-
Mansoura Faculty of Medicine
-
Fayoum Faculty of Medicine [2]
-
Assiut Faculty of Medicine
-
Suez Canal Faculty of Medicine
-
Minia Medical School
-
Monofia Faculty of Medicine
-
Sohag Faculty of Medicine
-
Tanta Faculty of Medicine
-
Arak University of Medical Sciences
-
Ardabil University of Medical Sciences
-
Azad University of Medical Sciences
-
Babol University of Medical Sciences, Babol
-
Baqiyatallah Medical Sciences University, Tehran
-
Birjand University of Medical Sciences
-
Bushehr University of Medical Sciences, Bushehr
-
Dezful University of Medical Sciences
-
Fasa Faculty of Medical Sciences, Fasa
-
Fatemiye University of Medical Sciences, Qom
-
Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan
-
Gonabad University of Medical Sciences, Gonabad
-
Gorgan University of Medical Sciences
-
Guilan University of Medical Sciences, Rasht
-
Hamedan University of Medical Sciences, Hamedan
-
Hormozgan University of Medical Sciences, Bandar Abbas
-
Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan
-
Medical University of Ilam
-
Iran University of Medical Sciences
-
Islamic Azad University Tehran Medical Branch
-
Islamic Azad University of Arak
-
Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Jahrom
-
Kashan University of Medical Sciences, Kashan
-
Kerman University of Medical Sciences, Kerman
-
Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah
-
Kordestan University of Medical Sciences, Sanandaj
-
Lorestan University of Medical Sciences, Khorramabad
-
Mashhad University of Medical Sciences
-
Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari
-
Medical University of Ilam, Ilam
-
Qazvin University of Medical Sciences, Qazvin
-
Qom University of Medical Sciences, Qom
-
Rafsanjan University of Medical Sciences, Rafsanjan
-
Sabzevar School of Medical Sciences, Sabzevar
-
Semnan University of Medical Sciences, Semnan
-
Shahed University of Medical Sciences, Tehran
-
Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences
-
Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences and Health Services
-
Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences
-
Shahroud University
-
Shiraz University
-
Tabriz University of Medical Sciences
-
Tehran University of Medical Sciences
-
Urmia University of Medical Sciences, Urmia (Oromieh)
-
Yasuj University of Medical Sciences
-
University of Duhok
-
Thi Qar University
-
University of Kirkuk
-
University of Baghdad
-
Al-Mustansiriya University
-
University of Mosul
-
University of Basrah
-
University of Anbar
-
Al-Mustansiriya University
-
University of Tikrit
-
Hawler Medical University
-
Al-Nahrain University
-
University of Anbar
-
University of Babylon
-
Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine
-
University of Kirkuk
-
University of Kirkuk
-
Hashemite University
-
Jordan University of Science and Technology
-
Mutah University
-
Yarmouk University
-
Kuwait University
-
Al-Balqa` Applied University
-
Lebanese University
-
Beirut Arab University
-
Saint Joseph University
-
University of Balamand
-
Lebanese American University
-
American University of Beirut
-
Holy Spirit University of Kaslik
-
Oman Medical College
-
Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar
-
King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences
-
King Abdulaziz University
-
University of Dammam
-
King Saud University
-
King Faisal University
-
Umm al-Qura University
-
Taif University
-
University of Hail
-
Tabuk University
-
Faculty of Medicine, Damascus University
-
Faculty of Medicine, University of Aleppo
-
Dubai Medical College for Girls
-
Gulf Medical University
-
University of Sharjah
-
Aden University
-
Hadhramout University of Science & Technology
-
Sana'a University
-
University of Science & Technology
TOP UNIVERSITIES IN ASIA
-
University of Tokyo
-
Peking University
-
National Taiwan University
-
Kyoto University
-
University of Hong Kong
-
Seoul National University
-
Zhejiang University (National Che Kiang University)
-
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
-
Nanyang Technological University
-
Chinese University of Hong Kong
-
Fudan University (Shanghai Medical University)
-
Tel Aviv University
-
University of Science & Technology of China
-
Osaka University
-
Korea Advanced Institute of Science & Technology KAIST
-
Nanjing University
-
Hebrew University of Jerusalem
-
Hong Kong University of Science & Technology
-
Tohoku University
-
City University of Hong Kong
-
Wuhan University
-
Hong Kong Polytechnic University
-
Harbin Institute of Technology
-
Huazhong University of Science & Technology
-
Sun Yat Sen University (Zhongshan University)
-
National Chiao Tung University
-
Nagoya University
-
Shandong University
-
Yonsei University
-
National Cheng Kung University
-
Technion Israel Institute of Technology
-
Xi'An Jiaotong University
-
National Tsing Hua University Taiwan
-
Korea University
-
Kyushu University
-
Hokkaido University
-
Tongji University
-
Weizmann Institute of Science
-
Tokyo Institute of Technology
-
Sichuan University
-
Keio University
-
Xiamen University
-
Jilin University
-
Southeast University
-
Beijing Normal University
-
University of Tsukuba
-
Tianjin University
-
Beihang University (Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics)
-
Central South University (Zhongnan University
-
Nankai University
-
Dalian University of Technology
-
Lanzhou University
-
South China University of Technology
-
Soochow University
-
Hanyang University
-
University of Malaya
-
Hiroshima University
-
Chongqing University
-
King Saud University
-
Sungkyunkwan University
-
Beijing Institute of Technology
-
Ben Gurion University of the Negev
-
National Central University
-
Kobe University
-
Waseda University
-
University of Tehran
-
Pohang University of Science & Technology
-
National Sun Yat Sen University
-
University of Electronic Science & Technology of China
-
East China Normal University
-
China Agricultural University
-
Pusan National University (Miryang)
-
East China University of Science & Technology
-
Hong Kong Baptist University
-
Kyungpook (Kyungbook) National University
-
Xidian University
-
Shanghai University
-
King Abdulaziz University
-
China University of Geosciences
-
Middle East Technical University / Orta DoÄŸu Teknik Üniversitesi
-
Bar Ilan University
-
National Yang-Ming University
-
Indian Institute of Technology Bombay
-
University of Science & Technology Beijing
-
Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics
-
Northwestern Polytechnical University
-
Mahidol University
-
Northeastern University China
-
Tamkang University
-
Beijing University of Chemical Technology
-
National Taiwan Normal University
-
Tehran University of Medical Sciences
-
Istanbul Technical University / Ä°stanbul Teknik Üniversitesi
-
Chulalongkorn University
-
Universiti Teknologi Malaysia
-
Hefei University of Technology
-
University of Haifa
-
Okayama University
Conference Highlights
- Radiology Trends and Technology
- Cancer & Therapeutics
- Neuroradiology and Neuro-oncology
- Cancer Cell Biology and Cancer Biomarker
- Medical Imaging Technology
- Clinical Radiology
- Radiography
- Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
- Radiation Oncology
- Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography- PET/CT
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Cancer Therapies
- Ultrasound
- Nuclear Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Oncology
- Molecular Imaging methodology
- Head and Neck Radiology
- Anesthesia
- Breast Cancer-Present Perspective
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- Pediatric Oncology
- Cancer Epigenetics
- Echocardiography
- Tumor Biology
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | July 16-17, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- OMICS Journal of Radiology
- Journal of Cancer Science & Therapy
- Journal of Oncology Research and Treatment
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by