Theme: Recent Progression and Innovation in Radiology and Oncology
Renowned Speakers
Radiology and Oncology 2021
With the coordination of organizing committee, “3rd Global Meeting on Oncology and Radiology” will be scheduled during October 26, 2021. focusing on the theme “Recent Progression and Innovation in Radiology and Oncology”. This Radiology and Oncology 2021 will focus on the theme “Shaping the future of Cancer Treatments” that provides a global platform to discuss about the present and future challenges across Breast Cancer, Ultrasound, Radiation Oncology, Cancer Epigenetics and Tumor Biology etc.
Radiology and Oncology 2021 provides you with a unique opportunity to meet up with peers from both academic circle and industries level belonging to Cancer and have been designed in an interdisciplinary manner with a multitude of tracks to choose from every segment and It explore creative technologies regarding Pediatric Oncology and Nuclear Medicine at the universal scale and aims to accomplish the targeted scientific sessions and recent advancements in the field of Cancer and Radiation. The goal of this conference is to deliver an outstanding program for exchange of ideas and authoritative views by leading professionals which covers the entire research related to Cancer Therapies, Echocardiography and beyond to confront the most challenging dilemmas in healthcare - and uncover new solutions.
Why to attend?
Radiology and Oncology 2021 is the platform where you can conflict experts, authorities and CROs from around the world. It’s your time to grab the opportunity to join Radiology and Oncology 2021 in a group of Speakers, discussion, Delegate, Poster, video proposal, Business Meetings, Networking and extra benefits for our Event Sponsor. The most recent approaches, upgrades, exchanging new ideas and research updates in Cancer and Radiopharmaceuticals are signs of this conference. The conference welcomes representatives from every educational institutes, clinical examination authority and symptomatic organizations to contribute their researches, giving a showcase of the new Cancer & Therapeutics procedures. It fills the gap between individuals and enterprises committed to advancing impactful innovations.
Target Audience:
- Oncologists
- Radiologists
- Radiation Oncologists
- Radiology Consultants
- Radiology and oncology Doctors
- Cancer therapists
- Radiographers and Radiology Technologists
- Healthcare professionals
- Research Scholar
- Founders and Employees of the related companies
- Clinical investigators & Researcher
- Hospitals and Health Services
- Pharmaceutical companies
- Laboratory members
- Students
- Support organizers
- Educators, Scientists, and Researchers
- Business Professionals
- Directors of Oncology and Radiology or related Programs or Associations
- Heads, Deans and Professors of Radiology and Oncology department
Track 1: Radiology Trends and Technology
Radiology is the science that uses restorative imaging to analyse diagnoses and sometimes also treat diseases inside the body. Two key trends seen all over the show floor that was remote-viewing systems for radiology images and technology streamlined to aid workflow efficiency. There was a proliferation of remote viewing systems to call up images on a Web-browser or ability to easily forward images from a PACS to referring physicians and for example, X-ray radiography, Computed tomography (CT), atomic pharmaceutical including Positron Emission Tomography (PET), and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are utilized to analyse or potentially treat infections
- Global radiology
- Medical radiography
- Radiation protection
- New approaches to sarcoma research
- Advanced laparoscopic surgery
- Pediatric radiology
- Nephrostomy
- Artificial intelligence
- Teleradiology
Track 2: Cancer & Therapeutics
Cancer Therapeutics is to tackle the challenge of tumor heterogeneity, cancer evolution and resistance to drug treatments which include an ever-increasing array of tools at the disposal of clinicians in their treatment of this disease. It has endured a paradigm shift away from the traditional cytotoxic drugs towards the targeting of proteins intimately involved in driving the cancer phenotype. Cancer therapeutics has pursued the discovery and development of HSP90 inhibitors, as one way of preventing or overcoming drug resistance. All Anticancer agents act by depressing cell multiplication or normal functioning, DNA synthesis and by blocking or changing RNA and protein metabolite.
- Cancer stem cells
- Kinase inhibitors
- Personalised medicine
- Protein–protein interactions
- Hormonal therapy
- Palliative therapy
- Drug therapy
- Gene therapy
- Clinical oncology
Track 3: Neuroradiology and Neuro-oncology
Neuroradiology mainly focus on the analysis and characterization of abnormalities of the peripheral and central nervous system, spine, and head and neck using neuroimaging techniques and study of radiology. Advances are raising all the more instantly in the exploration fields of Neuroradiology incorporates the improvement of MR imaging of the Brain and Spinal cord neoplasms. Essential imaging modalities incorporate Computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Ultrasound and Plain radiography are used on a constrained premise and in limited conditions, individual in the pediatric population. Neuro oncology is denounced to various malevolent disorders of neurons and is the subject of brain and spinal cord neoplasms, many of which are very dangerous and life-threatening that includes astrocytoma, glioblastoma multiform, ependymoma, pontine glioma and brain stem tumors. Cancer spreads to the Nervous System by direct invasion or compression from continuous tissues relates to the proximity of the Nervous System to other structures
- Clinical radiation oncology
- Radioactive compounds in neuroimaging
- Molecular radiation oncology
- Cellular radiation oncology
- Palliative radiotherapy in neuro oncology
- Intensity modulated radiation therapy(IMRT)
- Ganglioglio neurocytoma
- Central nervous system (CNS)
- Colloid cyst
- Surgical neuro oncology
- Ependymoma
- Whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT)
- Multivariate deposits in brain imaging
Track 4: Cancer Cell Biology and Cancer Biomarker
Cancer cells are cells that divide relentlessly, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and can be divided into many sub-topics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. Cells are the basic and smallest units of life that make up the human body. The study of cells is called cell biology. Certain cells may create a mass called a tumor. Cancer Biomarkers or the molecular markers are the biological molecules such as DNA, RNA, and Proteins, genes or the processes such as apoptosis and proliferation by which a specific disease, condition or any abnormalities in the body can be identified. It is a measurable indicator in a biological system and can be found in blood, tissues, specific organs, cell lines and in other body fluids.
- Cancerous cells
- Cell lung cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Benign tumor
- Diagnostic biomarker
- Squamous cell cancer of conjunctive
- Prognostic biomarker
- Brain cancer
- Stratification biomarker
Track 5: Medical Imaging Technology
Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities and is the technique of creating visual portrayal of the interior of a body for medical intervention and clinical analysis, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues. Imaging for therapeutic purposes includes a group which includes the administration of radiologists, radiographers, sonographers, medicinal physicists, biomedical designers, and other support staff working together to optimize the well-being of patients, each one in turn. Appropriate utilization of medical imaging requires a multidisciplinary approach.
- Medical ultrasonography
- Radiography
- Biological imaging
- Endoscopy
- Elastography
- Tomography
- Photoacoustic imaging
- Tactile imaging
- Functional near-infrared spectroscopy
Track 6: Clinical Radiology
Clinical radiology has been at the forefront of minimally invasive technique. It is a specialised branch of medicine that uses state of the art equipment and a range of techniques to capture images of the inside of the body and denotes to the usage of radiology to diagnose and treat injury or disease. X-ray, ultrasound, MRI and CT are used to model and direct a wide variety of interventional treatments throughout the body. Radiology is a major part of clinical practice through an extensive range of medical disciplines. It is typically the best, slightly invasive way of diagnosing, treating or monitoring disease and injury.
- Radiologists
- Interventional radiology
- Radiation therapists
- Medical radiation physicists
- Radiation oncology nurses
- Gynaecologic
- Chemotherapy
Track 7: Radiography
Radiography is the science of using radiation to contribute images of the tissues, organs, bones, and vessels that compose the human body. These images may be recorded on film or as a computerized image. Applications of radiography include medical radiography and industrial radiography. To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is composed by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays and other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition.
- Ultrasound
- Nuclear medicine
- Radiology
- Radiologic technologist
- Diagnostic medical sonographer
- Fluoroscopic procedures
Track 8: Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
Radiotherapy is a category of cancer treatment that uses beams of intense energy to kill cancer cells and most often uses X-rays, but protons or other types of energy also can be used. Radiation therapy uses waves of energy that include light or heat, to treat cancers and other tumors and conditions. It damages cells by destroying the genetic material that controls how cells grow and divide. Chemotherapy is most often used to treat cancer, since cancer cells grow and multiply much more quickly than most cells in the body and also a drug treatment that uses powerful chemicals to kill fast-growing cells in your body. Many different chemotherapy drugs are available and may be given with a curative intent, or it may goal to prolong life or to reduce symptoms
- Adjuvant therapy
- External beam radiation therapy
- Radiation oncology
- Chemotherapy regimen
- Neutropenic enterocolitis
- Brachytherapy
- Unsealed source radiotherapy
- Intraoperative radiotherapy
Track 9: Radiation Oncology
The field of radiation oncology covers the combination of radiotherapy in multimodal treatment procedures. Radiation oncology provides an open-access study for researchers and doctors concerned in the management and treatment of cancers cases, which brings together the advanced research and analysis in the field. Radiation can be given as a therapeutic system, either alone and in the mix with surgery or possibly chemotherapy. The Advances in Radiation Oncology is to give unique clinical research went for improving the lives of people living with tumor and distinctive ailments treated with radiation treatment.
- Medical radiation physicists
- Dosimetrists
- Proton therapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Radioembolization
- Radiation therapists
Track 10: Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography- PET/CT
Positron emission tomography scan is called as a PET scan and it is a type of test that may be used in cancer treatment and can be done along with a CT scan. It uses small amounts of radioactive materials which are known as radiotracers and radiopharmaceuticals, a special camera and a computer to evaluate organ and tissue functions. By identifying changes at the cellular level, PET may identified the early onset of disease before other imaging tests can. Nuclear medicine imaging procedures are non-invasive. With the exception of intravenous injections, they are usually painless. These tests use radioactive materials to evaluate medical conditions.
- Diagnose disease
- Trauma
- Positron-transmitting radionuclide
- Plan and guide interventional or therapeutic procedures
- Medical diagnosis
- Surgical planning
- Cyclotron
- Myocardial perfusion scan
Track 11: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to examine the anatomy and physiology of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body and based on sophisticated technology that excites and detects the change in the direction of the rotational axis of protons found in the water that makes up living tissues. It may be used to help diagnose or monitor treatment for a variety of conditions within the chest, abdomen and pelvis
- Tumor Heterogeneity
- Inter- intra tumour heterogeneity
- Claustrophobia
- Ionizing radiation of x-rays
- Radiation
- Computed Tomography
- Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE)
Track 12: Cancer Therapies
Cancer Treatments are medical therapies that asserted to treat cancer through different methods like surgery, chemotherapy, radiation oncology, and immunotherapy. Oncolytic biotherapy is a rising treatment procedure of cancer which uses infections to consume cancers. The recent development in genetic engineering techniques has been made using viruses to attack and destroy cancer cells ad it uses chemical substances or chemotherapeutics drug to kill the cancerous cells. Radiologists play an important role not only in developing and mastering endovascular genetic invasions but also in evaluating the progress of vascular gene therapy and reading further cultivation of vascular gene therapy technology
- Medical oncology
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery
- Molecular Targeted Cancer Therapies
- HDR Brachytherapy
- External beam radiation
- Stem cell Transplantation
- Hormone Therapies
- Immunotherapy
Track 13: Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a valuable methodology for observing the child's improvement in the uterus and aim is often to find a source of a disease or to exclude pathology. It utilizes high-frequency sound waves to catch live images from inside your body and help to guide biopsies, diagnose heart conditions, and assess damage after a heart attack. Ultrasound is non-invasive, safe and does not use ionizing radiation. Ultrasound imaging uses sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. It is used to help analyses the causes of pain, swelling and infection in the body's internal organs and to explore a baby in pregnant women and the brain and hips in infants
- Abdominal Ultrasound Imaging
- Pelvic Ultrasound Imaging
- Obstetric Ultrasound Imaging
- Ultrasound attenuation spectroscopy
- Medical ultrasonography
Track 14: Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear Medicine is a medical specialty that utilizations radioactive tracers to distinguish substantial capacities and to analyse and treat an infection. Nuclear medicine is a branch of radiology and therapeutic imaging. The unique way to kill malignancy cells with insignificant damage to encompassing tissue. It utilizes a smaller number of radioactive pharmaceuticals. This method help characterizes diseases in practically every organ system including the heart, mind, skeleton, thyroid and kidneys and many types of tumor and can be utilized to treat illness without surgery. This is one of a unique approach to kill cancer cells with minimal damage to surrounding tissue
- Endometrial cancer
- Single photon emission computed tomography
- Uterine cancer
- Nuclear medicine imaging
- Physiological imaging modality
- Positron emission tomography
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- Brachytherapy
Track 15: Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology is a medical specialty which provides minimally-invasive image-guided diagnosis and treatment of disease procedures using medical imaging guidance and also called as vascular and interventional radiology (VIR) which include x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. Although the procedure range performed by interventional radiologists is broad, the unifying concept behind these procedures is the application of image guidance and minimally invasive techniques in order to minimize risk to the patient
- Image guided cervical nerve root sleeve corticosteroid injection
- Carpal tunnel ultrasound and injection
- Image-guided liver biopsy
- Bursal injection
- Image-guided lumbar nerve root sleeve injection
- Biliary drainage
- Angioplasty and stent insertion
- Ascitic tap
- Uterine fibroid embolisation
Track 16: Oncology
Oncology is the branch of therapeutic science managing tumors, including the birthplace, advancement, determination, and medication that arrangements with the aversion, finding, and treatment of growth. It incorporates therapeutic oncology which uses chemotherapy, hormone treatment, and diverse prescriptions to treat malignancy, radiation oncology using radiation for treatment and surgical oncology. Distinctive tumors influencing diverse parts of the body e.g. blood cancer, prostate, lungs, platelets and different organs carry on in certain way are of various evaluations and cell write, react constantly to treatment and have diverse arrangement of compelling treatment regimen
- Neuro-Oncology
- Ocular oncology
- Thoracic oncology
- Gastrointestinal oncology
- Genitourinary oncology
- Gynecologic oncology
- Pediatric Oncology
- Hemato oncology
- Colorectal cancer
- Lung cancer
- Kidney cancer
Track 17: Molecular Imaging Methodology
Molecular imaging is a field of medical imaging that focuses on imaging molecules of medical interest and it enables the visualisation of the cellular function .The multiple and numerous potentialities of this field are applicable to the diagnosis of diseases that are cancer, neurological and cardiovascular diseases. This technique also contributes to improving the treatment of these disorders by optimizing the pre-clinical and clinical tests of new medication. This is in contrast to conventional methods for obtaining molecular information from preserved tissue samples, such as histology
- Atomic Force microscopy
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Optical imaging
- Near infrared imaging
- Single photon emission computed tomography
- Positron emission tomography
- Biomarkers
- Hyperpolarization
Track 18: Head and Neck Radiology
Head and Neck Radiology is the subspecialty devoted to the diagnostic imaging procedure and diagnosis of diseases of the head and neck. In radiology, the 'head and neck' refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal cord associated with vascular structures and encasing membranes. This includes x-rays, CT (computed tomography or CAT), Sonography, Mammography, Endoscopy, Ultrasound and MRI.
- Lymphatic system
- Nerve supply
- Cranial nerves
- Salivary glands
- Venous drainage
- Central nervous system
- Head and neck imaging
Track 19: Anesthesia
Anesthesia permit the painless performance of medical strategy with time and gained knowledge this term has become a sub discipline of medical science. Established medical guidelines are available for local and general anesthesia. Several factors are important during application of anesthesia protocol where patient’s age, exact disease condition etc. should be considered with care. Sedation suppresses is the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness.
- Cardiothoracic anesthesia
- Obstetric anesthesia
- Caesarean anesthesia
- Syndrome anesthesia
Track 20: Breast Cancer-Present Perspective
Breast cancer develops from a cancerous cell which develops in the lining of a mammary duct or a lobule in one of the breasts and most commonly presents as a lump that feels disparate from the rest of the breast tissue. More than 80% of cases are discovered when a person detects such a lump with the fingertips. It follows the classic progression though it often becomes systemic or widespread in the early onset of the disease. During this period, cancer may metastasize, or spread through lymphatics or bloodstream to areas elsewhere in the body
- Chemotherapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Molecular targeted cancer therapies
- HDR Brachytherapy
- Inflammatory breast cancer
- Phyllodes tumor
- Mammography
Track 21: Radiopharmaceuticals
A radiopharmaceutical is a medicine that can be used as a diagnosis and for therapeutic purposes. This is also a special class of drug and a combination of a radioactive molecule that has radioactivity. Radiopharmaceuticals consist of a radioactive isotope. Radioisotopes bind to biological molecules capable of targeting organs, tissues or specific cells of the human body. The representation of radiopharmaceuticals in clinical practice is increasing rapidly, which provides the medical association to have a greater way of detailed knowledge and information on the characteristics of various kinds of tumors.
- Radiopharmacology
- Medical isotopes
- Drug nomenclature
- Radioactive isotopes
- Easy and cheap to produce
- Not Toxic
- Myocardial Imaging
Track 22: Pediatric Oncology
Pediatric oncology is the speciality of medication that required with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer in children. It is one of the complicated sub-fields since the death rate connected with different malignancies is still high in children. The treatment of childhood cancer relies upon a few factors, including the stage and type of cancer, genetic factors and possible side effects of medicines, the family's preferences, and the child’s overall health and there is a high death rate still connected with different types of malignancies. The most common childhood cancer types include leukemia, brain tumors and lymphomas
- Colorectal Cancer
- Retinoblastoma
- Wilms tumor
- Neuroblastoma
- Lymphomas
- Brain tumors in children
- Immunotherapy
- Acute Leukaemia
- Chronic leukaemia
- Pleuropulmonary blastoma
- Ewing sarcoma
Track 23: Cancer Epigenetics
Epigenetics is a rapidly growing field of cancer research and Cancer Epigenetics deals with the epigenetic modifications to the DNA of cancer cells that do not comprise a change in the molecular processes nucleotide sequence than genetic mutations in a cell's transformation to cancer. It includes difference between normal cell and Tumor cell and analysis of nuclear organization, DNA methylation, Histone modification and the consequences of Genetic Mutations in genes encoding epigenetic regulators. DNA methylation patterns undergo complex changes in cancer
- Histone modification
- MicroRNA gene silencing
- Epigenetic carcinogenic
- Prostate cancer
- Cervical cancer
- Cancer genomics
- Cancer genome sequencing
- DNA methylation changes seen in cancer
Track 24: Echocardiography
Echocardiography is a painless test that uses sound waves to create moving pictures of the heart and uses standard two-dimensional, three-dimensional, and Doppler ultrasound to create images of the heart. The pictures show the size and shape of heart. They also show how well the heart's chambers and valves are working. Echo can detect possible blood clots inside the heart, fluid build-up in the pericardium and also can pinpoint areas of heart muscle that aren't contracting well due to poor blood injury from a previous heart attack
- Atrial fibrillation
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Heart block
- Tachy-brady syndrome
- Ventricular fibrillation
- Cardioversion
Track 25: Tumor Biology
Tumors grow in a series of steps and cancer cells behave as independent cells, growing without control to form tumors. Hyperplasia meaning that there are too many cells resulting from uncontrolled cell division. These cells appear normal, but often changes have occurred that result in some loss of control of growth. The discovery of tumor stem cells in a range of cancers has created opportunities for researchers to identify these rare cells in both solid tumors and hematologic cancers, as well as to investigate the role of these cells at different stages of disease. The recognition that the cancer cell is in a symbiotic relationship with the tumor microenvironment has created opportunities to study the interactions of cancer cells within the tumor or the host microenvironment
- Dysplasia
- Tumorigenesis
- carcinogenesis
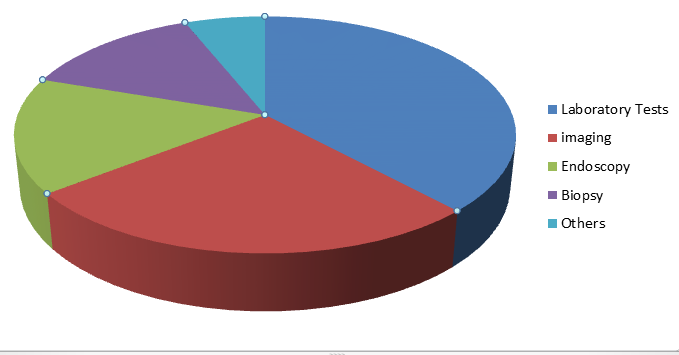
The screening type section incorporates research facility tests, imaging, endoscopy, biopsy, and others. Research facility tests incorporate testing of blood, pee, and other body liquids or tissue tests that assist with recognizing the presence of carcinogenic cells/tissue in the body. Research center tests for HCC finding incorporate Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood test, liver capacity test, other blood tests for the location of tumor markers and thickening elements, immunophenotyping, sputum cytology, urinalysis, and pee cytology. The previously mentioned tests help in identification of irregularities in cell and tissue structure.
Imaging tests assist with taking pictures of the inner organs to distinguish/affirm the presence of tumor. Accessible imaging tests for liver malignancy finding incorporate Computed Tomography (CT) check, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) examine, X-beam, ultrasound, and other radiographic tests. Moreover, MRI-viable pacemakers are currently accessible, which permit checking of patients with pacemakers. Patients with new viable pacemakers are just qualified for MRI imaging tests for disease conclusion. In this way, the imaging section is relied upon to witness a huge CAGR of 8.1% over the conjecture period. Other analytic tests incorporate biopsy, laparoscopy, and bone sweeps.
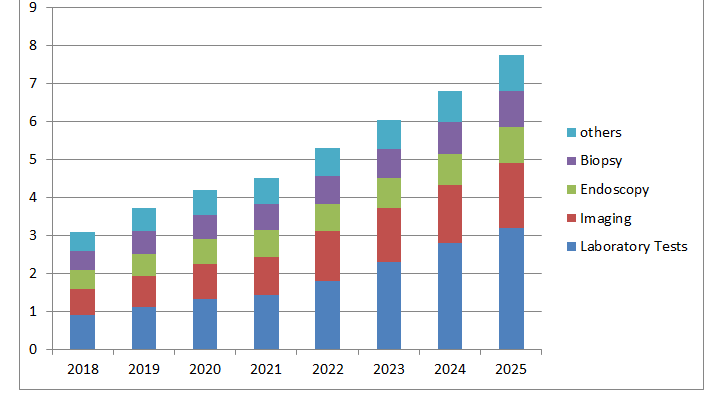
The worldwide liver disease symptomatic market size was esteemed at USD 8.25 billion of every 2017 and is projected to grow at a sound CAGR of 8.1% during the gauge time frame. Rising sickness rate, developing mindfulness, and expanded use of cutting edge malignancy screening items are a portion of the key elements pushing the market development. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the most widely recognized sort of essential liver disease in grown-ups. Different danger factors have been related with HCC, which incorporate hepatitis, weight, liquor initiated cirrhosis, openness to dietary afflation, and diabetes. It very well may be forestalled at a beginning phase by different screening techniques, for example, lab tests, imaging, and endoscopy. This is additionally increasing the market development.
Expanded predominance of malignant growth, selection of new discovery methods, and accessibility of productive disease medicines are likewise driving the market. What's more, steady government drives that assist with bringing issues to light in regards to the sickness and good repayment offices under the Affordable Care Act are boosting the market development. Exact recognition of the movement of malignant growth is fundamental for the determination of proper treatment regimens. As of now, the accessible tests show bogus positive outcomes now and again. Hence, corroborative tests are required, which builds the financial weight on patients.
Tests utilizing explicit biomarkers and tumor markers give relatively more exact outcomes. This presents a chance for industry members to foster tumor-explicit biomarkers and worked on demonstrative methodology for liver carcinoma. Neglected requirement for medicines giving total abatements and enduring reaction exists in the HCC space, which presents a solid chance to foster advancement first-in-class analytic methodology and treatments.
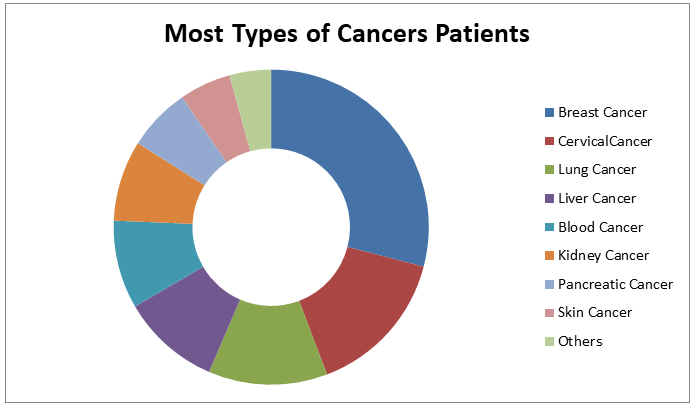
Cancer is a main source of death all throughout the planet. In the United States, it's the subsequent driving reason for death. Malignancy, which is a sickness brought about by unusual cells that gap and separate body tissue, can influence any piece of the body and can even spread to other body parts.
There are a few therapies that can make malignancy go into abatement, like chemotherapy. Sadly, these medicines are pricey as well as may not be accessible in certain countries. Far more atrocious, in any event, treating malignancy doesn't ensure that it will go into abatement. Many individuals pass on from this sickness even in the wake of being dealt with.
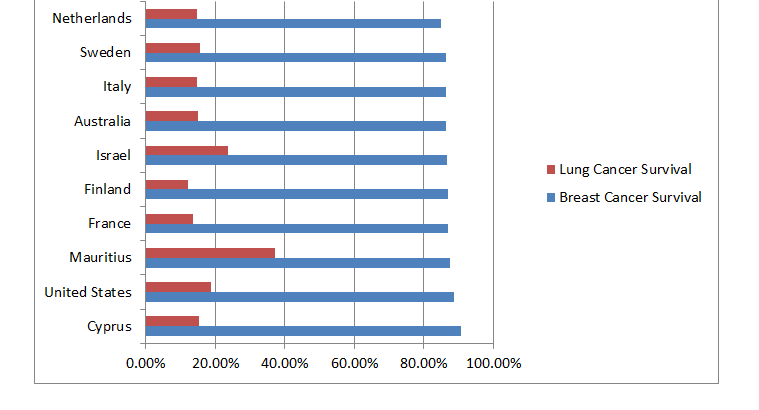
In certain countries, however, the shots at enduring malignancy are higher than in different regions all throughout the planet. A gathering of scientists saw endurance patterns all throughout the planet to rank countries by their individual disease endurance rates over a time of five years.
A few countries not on the rundown of generally speaking most elevated endurance rates positioned high when seeing explicit kinds of disease. For instance, countries in Southeast Asia including Japan and South Korea had the most noteworthy endurance rates for gastrointestinal tumors. Nonetheless, this equivalent area had a lot of lower endurance rates for different sorts of tumors, including skin melanoma.
Conference Highlights
- Interventional Radiology
- Cancer & Therapeutics
- Neuroradiology and Neuro-oncology
- Cancer Cell Biology and Cancer Biomarker
- Medical Imaging Technology
- Clinical Radiology
- Radiography
- Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy
- Radiation Oncology
- Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography- PET/CT
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Cancer Therapies
- Ultrasound
- Nuclear Medicine
- Interventional Radiology
- Oncology
- Molecular Imaging Methodology
- Anesthesia
- Head and Neck Radiology
- Breast Cancer-Present Perspective
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- Pediatric Oncology
- Cancer Epigenetics
- Echocardiography
- Tumor Biology
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 26-26, 2021 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- OMICS Journal of Radiology
- Journal of Integrative Oncology
- Journal of Clinical Oncology and Cancer Research
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by